COVID-19 Treatments
Access to COVID-19 treatments has significantly changed now that the federally funded Paxlovid™ program and other pandemic measures have ended. This webpage offers key updates and resources for prescribers and other healthcare providers to support safe and effective prescribing of COVID-19 antivirals, particularly Paxlovid™.
To find a pharmacy dispensing Paxlovid™ in Saskatchewan, see this interactive map.
Paxlovid™ Prescription
Paxlovid™ Prescription for LAEA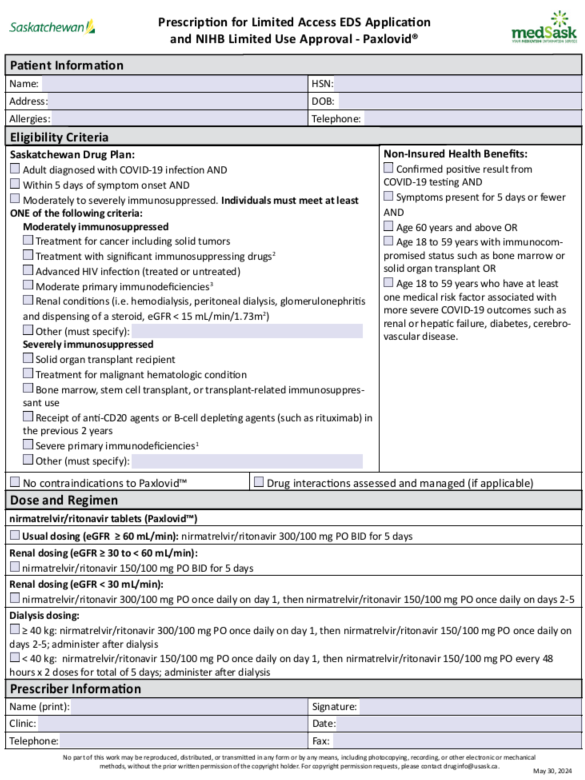 May 31, 2024 | Immunosuppressive Drugs May 31, 2024 |
Key Points
The landscape of COVID-19 has significantly changed.1,2 This is due in part to immunization, exposure from infection, and emergence of less virulent variants.2 The number of hospitalizations and deaths due to COVID-19 has decreased.3
- Most people, especially those with immunity, will have mild, self-limited COVID-19 disease.2
- Antivirals, like Paxlovid™, prevent hospitalization and death in people at high risk for progressing to severe COVID-19.1,4,5 Paxlovid™ does not help with symptom duration and severity.6
- Emerging evidence shows that moderately to severely immunosuppressed people are at the highest risk and are most likely to benefit from antivirals like Paxlovid™.1,5
Access to Antivirals
- COVID-19 Testing
Saskatchewan.ca Testing and Treatment Information
- Availability of Health Canada authorized rapid antigen self-tests:
- The federal government will no longer be supplying rapid antigen self-tests.
- COVID-19 self-tests are no longer being distributed to libraries, pharmacies, schools, or other retail outlets in Saskatchewan. Some locations may still have remaining stock of the federal supply available.
- Community pharmacies can purchase COVID-19 rapid antigen self-tests for sale from their wholesaler to sell to patients.
- The Saskatchewan government is evaluating options for testing with further communication to follow.
- Expiry dates of rapid antigen self-tests: Check the expiry date of tests as some federally supplied COVID-19 self-tests have expired. Most federally supplied tests will expire by Fall 2024.
- PCR testing: Can be ordered by physicians and nurse practitioners. Some facilities within the Saskatchewan Health Authority have access to point-of-care testing.
- Other links:
- Health Canada Testing for COVID-19 – general information about testing
- Health Canada Patient Guide to Self-testing
- Availability of Health Canada authorized rapid antigen self-tests:
- Access to COVID-19 Antivirals – Remdesivir & Paxlovid™
Saskatchewan.ca COVID-19 Treatments
Veklury® (remdesivir)
- Healthline 811 is no longer accepting referrals for COVID-19 antiviral therapy.
- Transplant and Oncology patients need to be referred to their specialist team.
- Some specialist prescribers/programs may have capacity to order and administer within Saskatchewan Health Authority facilities.
- Planning is underway to update the provincial order set and establish a pathway for access to remdesivir.
Paxlovid™ (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir)
- The no-cost federal supply of Paxlovid™ has expired as of May 31, 2024.
- Paxlovid™ is now procured like other prescription drug products:
- Physicians and nurse practitioners can prescribe Paxlovid™. Pharmacists are not authorized to prescribe Paxlovid™ at this time. (see Paxlovid™ Prescribing and Eligibility Criteria below.)
- Paxlovid™ is commercially available and will be ordered and dispensed by community pharmacies. See the Pharmacies Dispensing Paxlovid™ in Saskatchewan interactive map.
- Coverage of Paxlovid™ has transitioned away from the free federal program and depends on individual patient drug coverage.
- Paxlovid™ costs ~$1300.00 per course, which will now be paid by the Saskatchewan Drug Plan, Non-Insured Health Benefits (NIHB), private third-party insurance, or patient depending on the coverage that each patient has.
- Saskatchewan Drug Plan - Paxlovid™ is an exception drug status (EDS) benefit, with full coverage (100%) for people with Saskatchewan Health coverage who meet the EDS criteria (see Paxlovid™ Prescribing and Eligibility Criteria below).
- NIHB for First Nations and Inuit people – Paxlovid™ is a limited use benefit, with full coverage for those who meet the criteria. (see Paxlovid™ Prescribing and Eligibility Criteria below.)
- Private third-party insurance plans may also offer coverage. Third-party payors often follow provincial eligibility criteria, but coverage and eligibility may vary among plans.
- For Saskatchewan Drug Plan coverage, pharmacies that receive a prescription will submit the EDS request using the online Limited Access Exception Drug Status Application. Approval will be in real-time. Only participating pharmacies will be able to submit an online EDS claim. See the Pharmacies Dispensing Paxlovid™ in Saskatchewan interactive map.
- Paxlovid™ costs ~$1300.00 per course, which will now be paid by the Saskatchewan Drug Plan, Non-Insured Health Benefits (NIHB), private third-party insurance, or patient depending on the coverage that each patient has.
- Healthline 811 is no longer accepting referrals for COVID-19 antiviral therapy.
- Paxlovid™ Prescribing and Eligibility Criteria
- Healthline 811 is no longer accepting referrals for COVID-19 antiviral therapy.
- Transplant and Oncology patients need to be referred to their specialist team.
- Physicians and nurse practitioners can prescribe Paxlovid™.
- Saskatchewan pharmacists cannot prescribe Paxlovid™ at this time.
- Physicians and nurse practitioners will use the Paxlovid™ Prescription for LAEA to obtain Saskatchewan Drug Plan coverage for Paxlovid™. This form also includes the criteria for Non-Insured Health Benefits (NIHB) to facilitate coverage for First Nations and Inuit people.
- Pharmacies that receive a prescription will submit the EDS request using the online Limited Access Exception Drug Status Application (LAEA). Approval will be in real-time. Only pharmacies that dispense Paxlovid™ are able to access the LAEA and obtain coverage. See the Pharmacies Dispensing Paxlovid™ in Saskatchewan interactive map.
- Patients not eligible for Paxlovid™ should be reminded that Paxlovid™ only benefits people at high risk for hospitalization or death from COVID-19 infection. Paxlovid™ is not necessary for most people who are not high risk.
- AMMI Canada Practice Point: Updated recommendations for treatment of adults with symptomatic COVID-19 in 2023-2024
- UBC Therapeutics Initiative: How Useful is Paxlovid™ in 2024?
- AMMI Canada Practice Point: Updated recommendations for treatment of adults with symptomatic COVID-19 in 2023-2024
- Patients who do not need Paxlovid™ should be counselled on how to manage their symptoms at home and reminded to take measures to prevent the spread of their illness.
- medSask: At Home with COVID-19 Handout
- Centers for Disease Control: Respiratory Virus Guidance
Eligibility Criteria
Note that only Saskatchewan Drug Plan and NIHB criteria are listed here. Third-party payors often follow provincial eligibility criteria, but coverage and eligibility may vary among plans. Prescribers are advised to discuss cost and coverage with patients when prescribing.
Saskatchewan Drug Plan Eligibility Criteria for Paxlovid™
The eligibility criteria for Paxlovid™ have been updated to include only those individuals who are moderately to severely immunocompromised. The EDS criteria aligns with current evidence and Canada's Drug Agency recommendation.1
EDS criteria for Paxlovid™
- For the treatment of moderately or severely immunosuppressed adult patients diagnosed with COVID-19 infection. Paxlovid™ MUST be initiated within 5 days of symptom onset.
- Prescribers need to indicate the specific condition that confers immunosuppression.
- Examples of moderate immunosuppression may include:
- Treatment for cancer including solid tumors
- Treatment with significant immunosuppressing drugsb
- Advanced HIV infection (treated or untreated)
- Moderate primary immunodeficienciesc
- Renal conditions (i.e. hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, glomerulonephritis and dispensing of a steroid, eGFR < 15 mL/min/1.73m2)
- Other (to be specified by the prescriber)
- Examples of severe immunosuppression may include:
- Solid organ transplant recipients
- Treatment for malignant hematologic conditions
- Bone marrow, stem cell transplant, or transplant-related immunosuppressant use
- Receipt of anti-CD20 agents or B-cell depleting agents (such as rituximab) in the previous 2 years
- Severe primary immunodeficienciesa
- Other (to be specified by the prescriber)
a - Severe immunodeficiencies include combined immunodeficiencies affecting T cells, immune dysregulation (particularly familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis), or type 1 interferon defects (caused by a genetic primary immunodeficiency disorder or secondary to anti-interferon autoantibodies).
b - Immunosuppressing drugs such as a biologic in the past 3 months, oral immune-suppressing medication in the past months, oral steroid (20 mg/day of prednisone equivalent on an ongoing basis) in the past month, or immune-suppressing infusion or injection in the past 3 months.
c - Includes a primary immunodeficiency with a genetic cause at any time or a primary immunodeficiency due to immunoglobulin replacement therapy in the past year.
Non-Insured Health Benefits (NIHB) Eligibility Criteria for Paxlovid™
Paxlovid™ is a Limited Use Benefit. The NIHB drug benefit list can be accessed here.
Coverage criteria:
For the treatment of mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients at risk of progression to severe forms of the disease with:
- Confirmed positive result from COVID-19 testing; AND
- Symptoms present for 5 days or fewer; AND
- Age 60 years and above (no prior approval required); OR
- Age 18 to 59 years with immunocompromised status such as bone marrow or solid organ transplant; OR
- Age 18 to 59 years who have at least one medical risk factor associated with more severe COVID-19 outcomes such as renal or hepatic failure, diabetes, cerebrovascular disease.
- Healthline 811 is no longer accepting referrals for COVID-19 antiviral therapy.
- Paxlovid™ Distribution
Information about Paxlovid™ Distribution, Prescribing, and Assessment for pharmacies can be found on the Saskatchewan Drug Plan webpage.
Clinical Information
Prescribing Resources
- General Information about COVID-19
General Information about COVID-19
- Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Information for patients: Health Canada
Saskatchewan and Canada Epidemiology Data
- Government of Saskatchewan – Community Respiratory Illness Surveillance Program
- Government of Canada – COVID-19 epidemiology update
- Government of Canada – COVID-19 wastewater monitoring dashboard
COVID-19 Signs and Symptoms
Post-COVID/Long COVID
- COVID-19 for health professionals: Post COVID-19 condition
- Treatment of Mild-Moderate COVID-19
The following are general links for information about treating mild-moderate COVID-19. Consult local resources when considering the use of antivirals as eligibility criteria varies (see Paxlovid™ Prescribing and Eligibility Criteria above).
- BCCDC Practice Tool – Step-by-Step Assessment Guide for Clinicians
- Ontario Health – Recommendations for Antiviral Therapy for Adults with Mild to Moderate COVID-19
- AMMI Canada Practice Point - Updated recommendations for treatment of adults with symptomatic COVID-19 in 2023-2024
- RxFiles – COVID-19 Vaccines, Prevention and Therapies for Outpatients
- World Health Organization - A Living Guideline on Drugs for COVID-19
Paxlovid™
- Indications
- Paxlovid™ is indicated for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 disease in adults with a positive test and who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death.7
- People who are moderately to severely immunocompromised are at the highest risk for progressing to severe COVID-19. The clinical evidence to support this is best summarized in the Canada’s Drug Agency reimbursement review.
- Paxlovid™ does not reduce the risk of hospitalization or death in people that are not at risk of progression to severe disease.6
- Paxlovid™ has not been shown to reduce the duration of symptoms from COVID-19. The EPIC-SR trial showed a median time to symptom alleviation of 12 days in people who received Paxlovid™ and 13 days in people who received placebo.6
- The role of Paxlovid™ in post-COVID condition is unknown. Evidence is limited and has been inconsistent, with only a small benefit demonstrated in lowering the risk7 of post-COVID condition when Paxlovid™ is used during an acute infection. Research is ongoing.9
- Paxlovid™ is not approved for pre- or post-exposure prophylaxis.10
- Patients not eligible for Paxlovid™ should be reminded that Paxlovid™ only benefits people at high risk for hospitalization or death from COVID-19 infection. It is not necessary for people who are not high risk.
- AMMI Canada Practice Point: Updated recommendations for treatment of adults with symptomatic COVID-19 in 2023-2024
- UBC Therapeutics Initiative: How Useful is Paxlovid™ in 2024?
- Patients who do not need Paxlovid™ should be counselled on how to manage their symptoms at home and reminded to take measures to prevent the spread of their illness.
- medSask: At Home with COVID-19 Handout
- Centers for Disease Control: Respiratory Virus Guidance
- Contraindications and Cautions
Product Monograph
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity reaction - a history of clinically significant hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) or Stevens-Johnson syndrome) to its active ingredients (nirmatrelvir or ritonavir) or any other components of the product.7
- Drug interactions - concomitant use of drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening reactions or drugs that are potent CYP3A inducers where significantly reduced nirmatrelvir/ritonavir plasma concentrations may be associated with the potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance.7 See Drug Interactions.
- End-stage liver disease (Child-Pugh C or cirrhosis)7
Cautions
- Renal impairment – individuals with renal impairment need dose adjustment as follows:10
eGFR Dose 60 to < 90 mL/min no adjustment required
nirmatrelvir 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily for 5 days≥ 30 to < 60 mL/min nirmatrelvir 150 mg with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily for 5 days < 30 mL/min^ nirmatrelvir 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg once on day 1, then nirmatrelvir 150 mg with ritonavir 100 mg once daily on days 2-5* Dialysis^ ≥ 40 kg: nirmatrelvir 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg once on day 1, then nirmatrelvir 150 mg with ritonavir 100 mg once daily on days 2-5; administer after dialysis
< 40 kg: nirmatrelvir 150 mg with ritonavir 100 mg once on day 1, then nirmatrelvir 150 mg with ritonavir 100 mg every 48 hours x 2 doses; administer after dialysis^not recommended per product monograph. Dosing per clinical references (evidence from post-marketing)
*Some drug references include nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 150/100mg PO BID x 5 days for dosing in eGFR < 30 mL/min, which reflects a study where this dose was used in patients with Stage 4 CKD (eGFR 15 – 30 mL/min/1.73m2).11
For additional information: Ontario Health Paxlovid™ Use in Patients with Advanced CKD
- Pre-existing liver disease, liver enzyme abnormalities, hepatitis - hepatic transaminase elevations, clinical hepatitis, and jaundice have occurred in patients receiving ritonavir.7
- HIV drug resistance – use of Paxlovid™ may lead to a risk of HIV developing resistance to HIV protease inhibitors in individuals with uncontrolled or undiagnosed HIV-1 infection.7
- Drug interactions – concomitant use of medications metabolized by CYP3A or medications that inhibit or induce CYP3A must be reviewed with therapy not provided to patients with contraindicated interactions and other interactions appropriately managed.7 See Drug Interactions.
Special populations
Pediatrics: safety and efficacy have not been established in patients < 18 years of age.
- Saskatchewan Drug Plan coverage EDS criteria only includes adults as eligible for treatment with Paxlovid™. NIHB coverage criteria only includes adults aged 18 years and older.
- Not indicated for use in pediatrics per Canadian monograph7 however, the US FDA has approved use in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg with COVID-19 disease who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19.12
Pregnancy: limited data in pregnant people. Monograph suggests to not use in pregnant people unless the potential benefits outweigh the potential risk.7 Expert consensus (BCCDC, Ontario, NIH, ACOG) suggests that the use may be considered.9,13-15
Lactation: limited data in lactating people. Monograph suggests considering need for Paxlovid™, benefits of breastfeeding, and potential adverse effects.7 Expert consensus9,13-15 (BCCDC, Ontario, NIH) suggests that use may be considered. See LactMed for additional information.16
- Drug Interactions
- Both nirmatrelvir and ritonavir have several drug-drug interactions, some of which will require management and others which contraindicate the use of Paxlovid™.7
- Refer transplant patients and patients undergoing active cancer treatment to their specialist team for Paxlovid™ prescribing to ensure drug interactions with co-administered medications are managed appropriately.7,17,18
- A comprehensive evaluation of drug interactions (including prescription, non-prescription, and recreational drugs, and natural health products) is required when considering the use of Paxlovid™. Prescribers must manage drug interactions and communicate the management strategy to patients. Prescribers or pharmacists may need to follow up to ensure temporarily adjusted medications are correctly restarted.
Comprehensive drug interaction checker: University of Liverpool - COVID-19 Drug Interactions
Other resources to check and manage drug interactions:
- BCCDC - Practice Tool #3 - Drug-Drug Interactions and Contraindications – includes management strategy for patients on DOACs
- IDSA Management of Drug Interactions with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir
- Interactions checker in UpToDate Lexidrug (available via UpToDate Lexidrug [subscription] or via CPS [access via SHIRP])
- NatMed Pro (formerly Natural Medicines) (available via SHIRP)
- University Health Network – Paxlovid Prescribing & Drug Interaction Information
- University Health Network – Management of Paxlovid Drug Interactions in Oncology
- Product Monograph
Managing Drug Interactions
Ritonavir is a CYP 3A4 inhibitor7 and may decrease the metabolism of medications dependent on CYP 3A.
- In those medications that require CYP 3A4 for clearance, elevated concentrations may occur. This could result in a serious or life-threatening reaction.
- In those medications that require CYP 3A4 for activation, such as prodrugs, reduced concentrations may occur. This could result in a decreased therapeutic effect of the medication.
Nirmatrelvir and ritonavir are both major CYP 3A substrates:7
- CYP 3A inducers may increase metabolism of Paxlovid™ which results in potential for loss of virologic response and/or development of resistance.
Potential management strategies include:17,18
- Adjusting the dose of interacting medication
- Temporarily holding the interacting medication
- Stopping the interacting medication
- Using an alternative COVID-19 therapeutic (i.e.: remdesivir) or an alternative to the interacting medication
- Continuing the interacting medication with monitoring
Note that inhibition of CYP3A due to a Paxlovid™ interaction lasts about 2 days after stopping Paxlovid™.17Dose adjustments, holding the interacting medication, or use of an alternative should occur for the entire course of Paxlovid™, plus 2 additional days after stopping, for a total of 7 days.17
Remember: a drug interaction in the table deemed “manageable” does not necessarily mean it is manageable for every patient. Consider additional patient factors that affect their ability to properly manage the drug interaction, such as:
- Do they understand which medication to hold or to split in half?
- Are they able to split the tablet themselves?
- Do they receive compliance packs which require manipulating?
- Do they comprehend when to restart their medication?
Notable/common drug interactions (not exhaustive):
- Special attention is warranted when co-administering Paxlovid™ with medications that have a narrow therapeutic window:7,17
- Anticoagulants (apixaban, rivaroxaban, warfarin)
- Anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, primidone)
- Antiarrhythmics (amiodarone, disopyramide, dronedarone, flecainide, propafenone, quinidine)
- Digoxin
- Opioids (particularly fentanyl)
- Medications that reduce levels of Paxlovid™:17
- Rifampin
- St John’s Wort
- Interactions where stopping or switching may not be appropriate:17
- Bosentan, sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil (for pulmonary hypertension)
- Clopidogrel, ticagrelor
- Clozapine
- Eplerenone
- Lurasidone, pimozide, quetiapine
- Combination oral contraceptives (patients are encouraged to use additional protection while using Paxlovid™ because levels of estrogen are reduced)
- Certain benzodiazepines
- Salmeterol
- Felodipine, nifedipine
- Ivabradine
- Others17
- Some statins
- PDE4 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction
- Domperidone
- Dihydroergotamine
- Additional Clinical Information
Within 5 days and for 5 days: Paxlovid™ is recommended within 5 days of symptom onset. Data from EPIC HR comparing earlier (<3 days) to later (3–5 days) treatment showed no difference in efficacy.2 Studies looking at people treated with Paxlovid™ beyond 5 days of symptom onset showed Paxlovid™ only works well when given within 5 days of symptom onset.19 Paxlovid™ is used for a total of 5 days. The benefit of extended courses or additional courses is uncertain.2
Paxlovid™ rebound: some people report a return of symptoms and test positivity a few days after completing a course of Paxlovid™. This may occur whether or not Paxlovid™ has been used.10,20 Recurrent symptoms are generally mild.20 Retreatment with Paxlovid™ is not routinely recommended, especially if symptoms are improving, but may be considered in people with significant or rapidly progressing symptoms.20,21
Side effects: most commonly reported side effects are dysgeusia (5%) and diarrhea (3%). Other side effects include nausea, vomiting, headache, malaise, and hypertension.7,10
Contact Us
- medSask for Clinical Questions
For questions about the clinical use of Paxlovid™, contact medSask.
Email: druginfo@usask.ca
Phone Numbers:
- 1-800-667-3425 (Saskatchewan)
- 306-966-6340 (Saskatoon)
- Drug Plan and Extended Benefits Branch (DPEBB) for Eligibility or Pharmacy Billing Questions
For questions about Saskatchewan Drug Plan eligibility or pharmacy billing, contact DPEBB.
Email: DPEBimmunizations@health.gov.sk.ca
Phone Numbers:
- 1-800-667-7581 (Saskatchewan)
- 306-787-3317 (Regina)
Pharmacies interested in dispensing Paxlovid™ can register with DPEBB by emailing DPEBimmunizations@health.gov.sk.ca .
References
- References
- Canadian Journal of Health Technologies. CADTH Reimbursement Recommendation Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir (Paxlovid). 2024;4(4):1-23. Accessed May 29, 2024. https://www.cadth.ca/sites/default/files/DRR/2024/SR0808%20Paxlovid%20-%20Final%20Rec.pdf
- Grant JM, Lam J, Goyal SV, et al. AMMI Canada Practice Point: Updated recommendations for treatment of adults with symptomatic COVID-19 in 2023-2024. J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can. 2024;8(4):245-252. Published 2024 Jan 16. doi:10.3138/jammi-2023-12-07. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10797770/
- COVID-10 epidemiology update: Summary. Health Infobase. Government of Canada. Updated May 21, 2024. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://health-infobase.canada.ca/covid-19/
- Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1397-1408. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35172054/
- Dormuth CR, Kim JD, Fisher A, Piszczek J, Kuo IF. Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and COVID-19 Mortality and Hospitalization Among Patients With Vulnerability to COVID-19 Complications [published correction appears in JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Feb 5;7(2):e241976]. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(10):e2336678. Published 2023 Oct 2. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.36678. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37782496/
- Hammond J, Fountaine RJ, Yunis C, et al. Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with Covid-19. New England Journal of Medicine. 2024 Apr 4;390(13):1186-95. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2309003
- Paxlovid. Product Monograph. Pfizer Canada ULC. Updated January 17, 2022. Accessed May 28, 2024. https://pdf.hres.ca/dpd_pm/00073991.P
- Xie Y, Choi T, Al-Aly Z. Association of Treatment With Nirmatrelvir and the Risk of Post-COVID-19 Condition. JAMA Intern Med. 2023 Jun 1;183(6):554-564. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.0743. PMID: 36951829; PMCID: PMC10037200.
- Ontario Health. Frequently asked questions on antiviral therapy for adults with mild to moderate COVID-19. Updated April 2, 2024. Accessed May 27, 2024. https://www.ontariohealth.ca/sites/ontariohealth/files/FAQs-on-Antiviral-Therapy-for-Adults-with-Mild-to-Moderate-COVID-19.pdf
- Nirmatrelvir and Ritonavir. UpToDate Lexidrug. Wolters Kluwer. Updated May 21, 2024. Accessed May 27, 2024. https://online-lexi-com/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/patch_f/7185660?c…
- Cho WJ, Harden D, Moreno D, et al. Oral antiviral therapies for COVID-19 in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease or kidney failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2023;38(8):1912-1914. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfad058
- Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers: Emergency Use Authorization for Paxlovid™. Updated March 2024. Accessed May 28, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download
- British Columbia COVID Therapeutics Committee. Practice tool – step-by-step assessment guide for clinicians. Updated May 2024. Accessed May 27, 2024. http://www.bccdc.ca/Health-Professionals-Site/Documents/COVID-treatment/PracticeTool1_AssessmentGuideforClinicians.pdf
- National Institutes of Health. Pregnancy, Lactation, and COVID-19 Therapeutics. Updated February 29, 2024. Accessed May 28, 2024. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/special-populations/pregnancy/pregnancy-lactation-and-covid-19-therapeutics/
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. COVID-19 FAQs for obstetricians-gynecologists, obstetrics. Washington, DC: ACOG; 2020. Available at: https://www.acog.org/clinical-information/physician-faqs/covid-19-faqs-for-ob-gyns-obstetrics . Retrieved May 28, 2024.
- National Library of Medicine. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-. Accessed May 28, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501922/.
- British Columbia COVID Therapeutics Committee. Practice tool – drug-drug interactions and contraindications. Updated May 22, 2024. Accessed May 27, 2024. http://www.bccdc.ca/Health-Professionals-Site/Documents/COVID
- University of Liverpool. Covid-19 Drug Interactions; Interaction checker. c2024. https://www.covid19-druginteractions.org/checker
- Wang Y, Zhao D, Liu X, Chen X, Xiao W, Feng L. Early administration of Paxlovid reduces the viral elimination time in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants. J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28443. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28443. PMID: 36579782; PMCID: PMC9880690.)
- Cohen P, Gebo K. COVID-19: Management of adults with acute illness in the outpatient setting. UpToDate. Wolters Kluwer. Updated April 19, 2024. Cited May 27, 2024. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/covid-19-management-of-adults-with-acute-illness-in-the-outpatient-setting
- National Institutes of Health. Ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid). COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. Updated February 29, 2024. Accessed May 27, 2024. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/about-the-guidelines/whats-new/
No part of this work may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the copyright holder. For copyright permission requests, please contact druginfo@usask.ca.
May 30, 2024